Alzheimer’s vaccine enters human trials aiming to stop disease before symptoms begin

John E. Kaye
- Published
- News, Technology
A new Alzheimer’s vaccine designed to stop the disease before symptoms appear is entering human clinical trials in the United States
The treatment, called Duvax, targets both amyloid-beta and tau—the two key proteins linked to the development of Alzheimer’s—and is intended for people at risk of the disease but who have not yet shown cognitive decline.
Alzheimer’s is the most common cause of dementia, affecting an estimated 55 million people worldwide, with 10 million new cases diagnosed each year.
In the UK alone, nearly one million people are living with dementia, and Alzheimer’s accounts for around two-thirds of those cases.
Despite decades of research, no treatment has yet been shown to prevent the disease before symptoms begin.
Unlike existing therapies that attempt to slow progression once memory and cognition are already affected, Duvax is being developed as a secondary prevention therapy.
It is designed for use during the “preclinical” stage, when abnormal proteins are already accumulating in the brain but before irreversible neurological damage has set in.
The vaccine uses an immunotherapy approach to train the body’s immune system to recognise and clear harmful forms of amyloid and tau.
Its use is guided by blood tests that can detect these early pathological changes—allowing for timely intervention and the possibility of halting the disease in its tracks.
The Phase 1 trial will assess the safety and immunogenicity of Duvax in humans. It is backed by a $3 million grant from the US National Institutes of Health (NIH), awarded through the agency’s SBIR Fast-Track programme.
An initial portion of the grant has been released to begin the trial, with the remainder expected later in 2025.
Nuravax, a clinical-stage biotech company focused on neurodegenerative disorders, is leading the development, regulatory work and manufacturing of the vaccine, which is licensed from the non-profit Institute for Molecular Medicine (IMM). The underlying technology is based on IMM’s MultiTEP platform, a modular vaccine system adaptable to DNA, RNA and recombinant protein formats.
If successful, Duvax would become the first vaccine to target both of Alzheimer’s core drivers in people with no symptoms, offering a potential shift from treatment to prevention in one of the most challenging areas of modern medicine.
Roman Kniazev, CEO of Nuravax, said: “This SBIR grant is a powerful endorsement of our mission to clinically validate and advance Duvax as a first-in-class vaccine for Alzheimer’s prevention.
“While IMM laid the scientific foundation, our focus at Nuravax is on translating that innovation into real-world impact. This funding enables us to move Duvax into clinical trials in the U.S. and brings us one step closer to delivering it as preventive therapy for individuals at risk – before symptoms begin.”
The need for early intervention has grown increasingly urgent as the global population ages. By 2050, the number of people living with dementia is expected to more than triple, reaching over 150 million. While some new drugs have been approved in recent years to target amyloid plaques in diagnosed patients, their effects are modest, and treatment must begin early to have any measurable benefit.
Dr Michael Agadjanyan, Vice President of the Institute for Molecular Medicine and Head of Immunology, said the trial represented a critical turning point after years of foundational research.
“The Phase 1 trial, supported by this SBIR grant awarded to our development and commercialization partner, Nuravax, marks a critical step in translating years of foundational research at IMM into a potential clinical breakthrough,” he said.
“Based on strong preclinical data, we at IMM expect Duvax to elicit a robust immune response against both Aβ and tau pathologies, an approach that could fundamentally shift the paradigm of Alzheimer’s treatment from symptomatic and disease-modifying treatment (DMT) to secondary preventive therapy for cognitively unimpaired people at risk of disease.”
Main photo: Anna Shvets/Pexels
RECENT ARTICLES
-
 Deepfake celebrity ads drive new wave of investment scams
Deepfake celebrity ads drive new wave of investment scams -
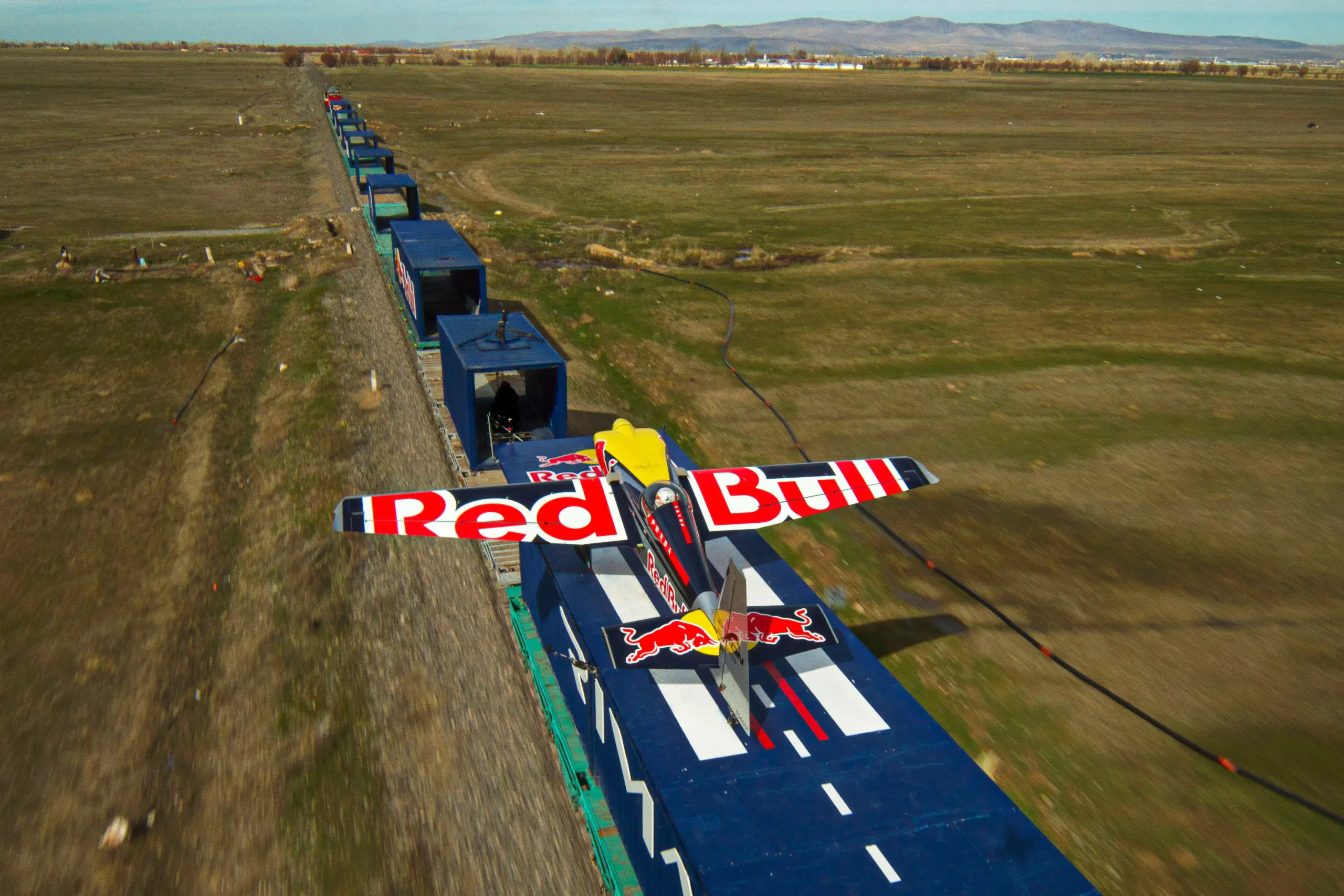
 WATCH: Red Bull pilot lands plane on moving freight train in aviation first
WATCH: Red Bull pilot lands plane on moving freight train in aviation first -
 Europe eyes Australia-style social media crackdown for children
Europe eyes Australia-style social media crackdown for children -
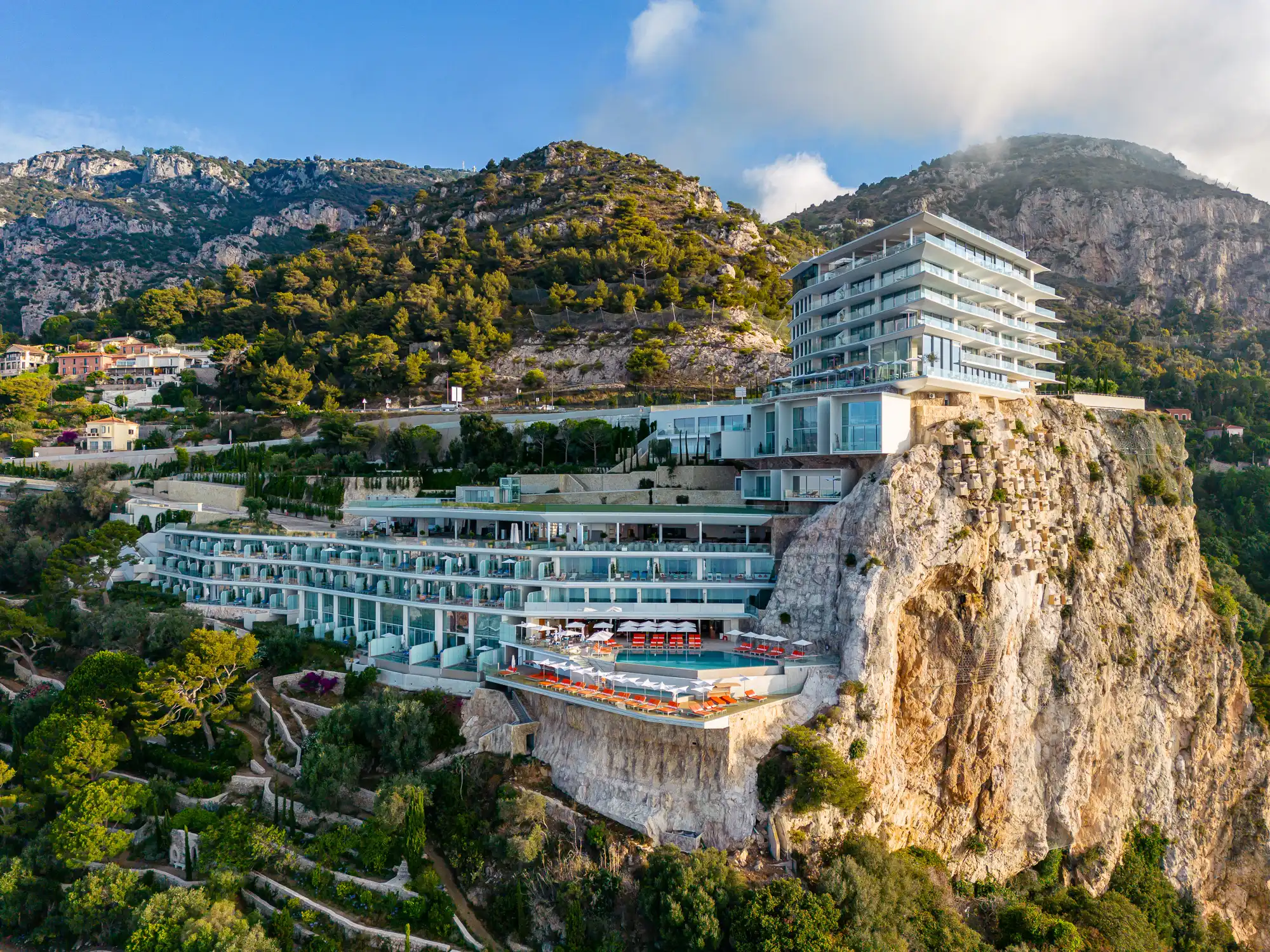
 These European hotels have just been named Five-Star in Forbes Travel Guide’s 2026 awards
These European hotels have just been named Five-Star in Forbes Travel Guide’s 2026 awards -
 McDonald’s Valentine’s ‘McNugget Caviar’ giveaway sells out within minutes
McDonald’s Valentine’s ‘McNugget Caviar’ giveaway sells out within minutes -
 Europe opens NanoIC pilot line to design the computer chips of the 2030s
Europe opens NanoIC pilot line to design the computer chips of the 2030s -
 Zanzibar’s tourism boom ‘exposes new investment opportunities beyond hotels’
Zanzibar’s tourism boom ‘exposes new investment opportunities beyond hotels’ -
 Gen Z set to make up 34% of global workforce by 2034, new report says
Gen Z set to make up 34% of global workforce by 2034, new report says -
 The ideas and discoveries reshaping our future: Science Matters Volume 3, out now
The ideas and discoveries reshaping our future: Science Matters Volume 3, out now -
 Lasers finally unlock mystery of Charles Darwin’s specimen jars
Lasers finally unlock mystery of Charles Darwin’s specimen jars -
 Strong ESG records help firms take R&D global, study finds
Strong ESG records help firms take R&D global, study finds -
 European Commission issues new cancer prevention guidance as EU records 2.7m cases in a year
European Commission issues new cancer prevention guidance as EU records 2.7m cases in a year -
 Artemis II set to carry astronauts around the Moon for first time in 50 years
Artemis II set to carry astronauts around the Moon for first time in 50 years -
 Meet the AI-powered robot that can sort, load and run your laundry on its own
Meet the AI-powered robot that can sort, load and run your laundry on its own -
 Wingsuit skydivers blast through world’s tallest hotel at 124mph in Dubai stunt
Wingsuit skydivers blast through world’s tallest hotel at 124mph in Dubai stunt -
 Centrum Air to launch first European route with Tashkent–Frankfurt flights
Centrum Air to launch first European route with Tashkent–Frankfurt flights -
 UK organisations still falling short on GDPR compliance, benchmark report finds
UK organisations still falling short on GDPR compliance, benchmark report finds -
 Stanley Johnson appears on Ugandan national television during visit highlighting wildlife and conservation ties
Stanley Johnson appears on Ugandan national television during visit highlighting wildlife and conservation ties -
 Anniversary marks first civilian voyage to Antarctica 60 years ago
Anniversary marks first civilian voyage to Antarctica 60 years ago -
 Etihad ranked world’s safest airline for 2026
Etihad ranked world’s safest airline for 2026 -
 Read it here: Asset Management Matters — new supplement out now
Read it here: Asset Management Matters — new supplement out now -
 Breakthroughs that change how we understand health, biology and risk: the new Science Matters supplement is out now
Breakthroughs that change how we understand health, biology and risk: the new Science Matters supplement is out now -
 The new Residence & Citizenship Planning supplement: out now
The new Residence & Citizenship Planning supplement: out now -
 Prague named Europe’s top student city in new comparative study
Prague named Europe’s top student city in new comparative study -
 BGG expands production footprint and backs microalgae as social media drives unprecedented boom in natural wellness
BGG expands production footprint and backs microalgae as social media drives unprecedented boom in natural wellness



























